前言:Hello大家好,我是小哥谈。损失函数(loss function)是机器学习中用来衡量模型预测值与真实值之间差异的函数。它用于度量模型在训练过程中的性能,以便优化模型参数。在训练过程中,损失函数会根据模型的预测结果和真实标签计算出一个标量值,代表了模型预测的错误程度。通过最小化损失函数,可以使模型的预测结果与真实值之间的差距变小,从而提升模型的性能。本节课就简单介绍一下常见的IoU损失函数并重点讲解如何去更换损失函数!🌈
 前期回顾:
前期回顾:
YOLOv5算法改进(1)— 如何去改进YOLOv5算法
YOLOv5算法改进(2)— 添加SE注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(3)— 添加CBAM注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(4)— 添加CA注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(5)— 添加ECA注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(6)— 添加SOCA注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(7)— 添加SimAM注意力机制
YOLOv5算法改进(8)— 替换主干网络之MobileNetV3
YOLOv5算法改进(9)— 替换主干网络之ShuffleNetV2
YOLOv5算法改进(10)— 替换主干网络之GhostNet
YOLOv5算法改进(11)— 替换主干网络之EfficientNetv2
YOLOv5算法改进(12)— 替换主干网络之Swin Transformer
YOLOv5算法改进(13)— 替换主干网络之PP-LCNet
YOLOv5算法改进(14)— 更换Neck之BiFPN
YOLOv5算法改进(15)— 更换Neck之AFPN
YOLOv5算法改进(16)— 增加小目标检测层
目录
🚀1.不同IoU的介绍
🚀2.YOLOv5源码中的损失函数
🚀3.EIoU
💥💥3.1 简介
💥💥3.2 添加步骤
🚀4.AlphaIoU
💥💥4.1 简介
💥💥4.2 添加步骤
🚀5.SIoU
💥💥5.1 简介
💥💥5.2 添加步骤
🚀6.WIoU
💥💥6.1 简介
💥💥6.2 添加步骤
说明:♨️♨️♨️
关于损失函数(IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU和EIoU) ,请参考本专栏文章:
YOLOv5基础知识入门(5)— 损失函数(IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU和EIoU)
🚀1.不同IoU的介绍
本节课正式开始之前,先简单介绍一下不同IoU的区别:👇
IOU Loss:主要考虑检测框和目标框重叠面积。
GIOU Loss:在IOU的基础上,解决边界框不相交时loss等于0的问题。
DIOU Loss:在IOU和GIOU的基础上,考虑边界框中心点距离的信息。
CIOU Loss:在DIOU的基础上,考虑边界框宽高比的尺度信息。
EIOU Loss:在CIOU的基础上,解决了纵横比的模糊定义,并添加Focal Loss解决BBox回归中的样本不平衡问题。
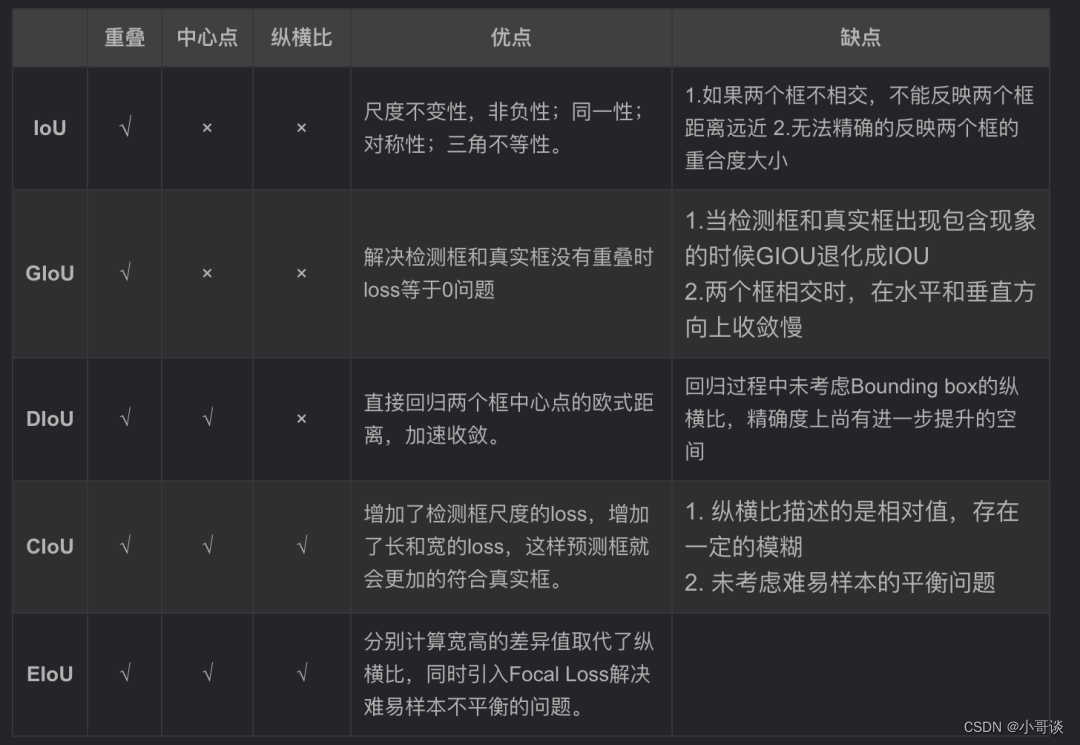
AlphaIoU Loss:基于IoU进行扩展,通过引入一个可调参数alpha来平衡正样本和负样本之间的权重。当alpha为0时,AlphaIoU Loss退化为普通的IoU Loss;当alpha为1时,AlphaIoU Loss主要关注正样本的损失。
SIoU Loss:结合了IoU(Intersection over Union)和GIoU(Generalized IoU)两种损失函数的优点,可以更好地衡量目标框的预测准确度。具体来说,SIoU损失通过计算预测框和真实框之间的IoU,并将其转化为一个连续可导的数值。与IoU不同的是,SIoU考虑了目标框的位置偏移和大小偏移,使得模型更加关注目标框的准确匹配。
WIoU Loss:在IoU Loss基础上引入了类别权重,以更好地处理多类别目标检测问题。具体来说,对于每个类别,WIoU Loss计算各个预测框与真实框的IoU,然后根据类别权重对IoU进行加权求和得到最终的损失值。
🚀2.YOLOv5源码中的损失函数
在YOLOv5源码中,应用了上述某些损失函数,具体位置位于utils / metrics.py文件,bbox_iou函数中。具体如下图所示:👇
接下来,我们重点看下该函数:
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):通过这行代码我们可以看出,当GIoU、DIoU、CIoU的布尔值都为False的时候,会返回最普通的IoU,如果其中有一项的布尔值为True,即返回设定为True的该IoU。
通常用utils / metrics.py文件下的__call__函数计算回归损失(bbox损失),由下图可知,YOLOv5中的bbox_iou默认使用的是CIOU Loss。
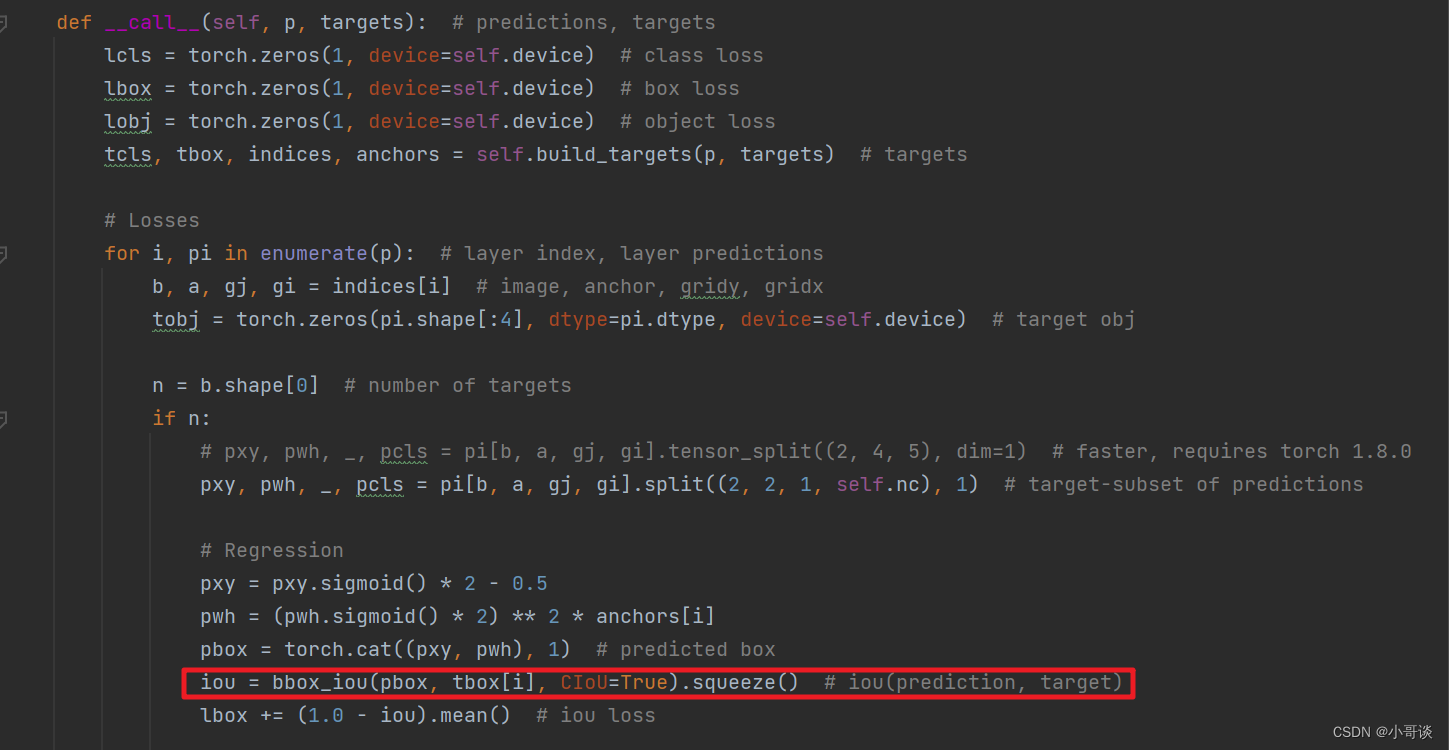
🚀3.EIoU
💥💥3.1 简介
EIoU Loss是目标检测任务中用于评估边界框预测的一种损失函数。EIoU(Enhanced Intersection over Union)是IoU(Intersection over Union)的一种改进版本,它在计算交并比时考虑了更多的因素,以提高边界框预测的准确性。
IoU是通过计算检测框和真实框的交集面积与并集面积之比来评估检测的准确性。然而,IoU存在一些问题,例如在两个框之间有重叠但不完全重叠时,IoU可能会不准确地估计框的质量。为了解决这个问题,EIoU引入了一个偏移项和一个缩放项。偏移项用于衡量预测框和真实框中心点之间的偏移,而缩放项用于衡量预测框和真实框尺寸之间的缩放关系。通过考虑这些因素,EIoU可以更准确地评估边界框预测的质量。
作用:
🍀(1)将纵横比的损失项拆分成预测的宽高分别与最小外接框宽高的差值,加速了收敛提高了回归精度。
🍀(2)引入了Focal Loss优化了边界框回归任务中的样本不平衡问题,即减少与目标框重叠较少的大量锚框对BBox回归的优化贡献,使回归过程专注于高质量锚框
公式:
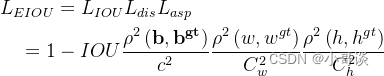
其中 ,Cw 和 Ch 是覆盖预测框真实框的最小外接框的宽度和高度。
从 EIOU 损失函数公式可以看出,EIOU 损失函数包含三个部分:预测框和真实框的重叠损失LIou,预测框和真实框的中心距离损失Ldis,预测框和真实框的宽和高损失Lasp。EIOU 损失的前两部分延续 CIOU 中的方法,但是宽高损失直接使预测框与真实框的宽度和高度之差最小,使得收敛速度更快。
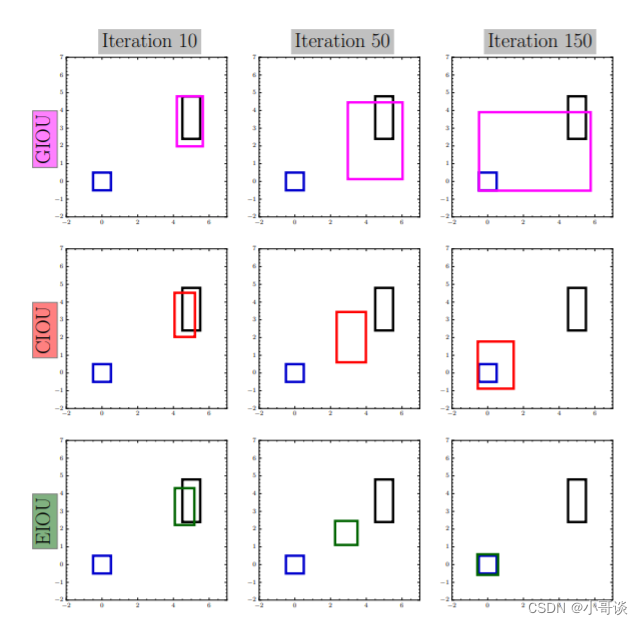
下图是 GIOU、CIOU 和 EIOU 损失预测框的迭代过程对比图,红色框和绿色框就是预测框的回归过程,蓝色框是真实框,黑色框是预先设定的锚框,可以看出 CIOU 的问题是宽和高不能同时增大或者减少,而 EIOU 可以。

论文题目:《Focal and Efficient IOU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression》
论文地址: Focal and Efficient IOU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression
💥💥3.2 添加步骤
步骤1:配置metrics.py文件
将utils / metrics.py文件中的bbox_iou函数全部替换成如下代码:
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, EIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns the IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU or EIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU or EIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 +
(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center distance squared
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
elif EIoU:
rho_w2 = ((b2_x2 - b2_x1) - (b1_x2 - b1_x1)) ** 2
rho_h2 = ((b2_y2 - b2_y1) - (b1_y2 - b1_y1)) ** 2
cw2 = cw ** 2 + eps
ch2 = ch ** 2 + eps
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + rho_w2 / cw2 + rho_h2 / ch2)
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
else:
return iou # IoU
步骤2:配置loss.py文件
在utils / loss.py文件中找到__call__函数,将Regression loss中计算IoU的代码(如下图所示)。
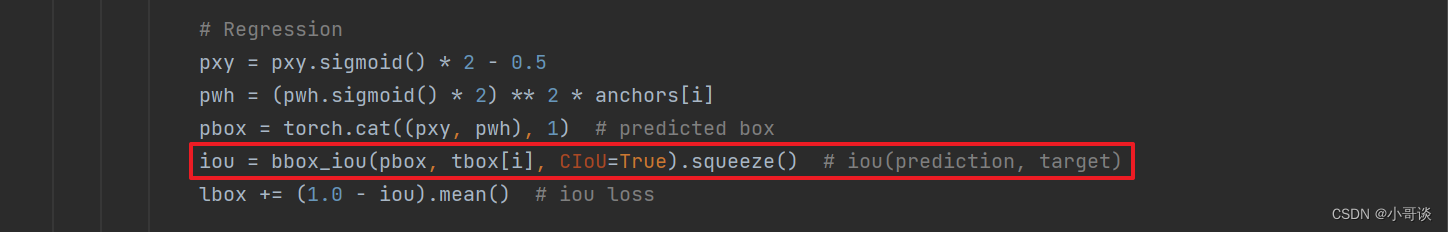
换成下面这句:
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, CIoU=False, EIoU=True) 🚀4.AlphaIoU
💥💥4.1 简介
AlphaIoU是一种目标检测中常用的评估指标,用于衡量预测框和真实标注框之间的相似度。IoU(Intersection over Union)衡量的是两个框之间的重叠程度,而AlphaIoU则引入了一个参数alpha,用于调整重叠部分和非重叠部分对最终相似度的贡献度。
在实际应用中,通常需要根据具体情况进行尝试和调整。可以通过在验证集或测试集上进行实验,使用不同的alpha值进行评估和比较,选择效果最好的参数。
公式:
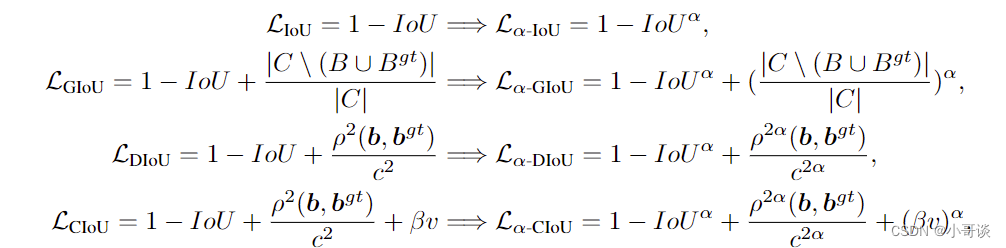
论文题目:《Alpha-IoU: A Family of Power Intersection over Union Losses for Bounding Box Regression》
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.13675.pdf
💥💥4.2 添加步骤
步骤1:配置metrics.py文件
将utils / metrics.py文件中的bbox_iou函数全部替换成如下代码,由论文可知,alpha=3的时候效果最好,所以我们将alpha的值设置为3。
def bbox_alpha_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=False, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, alpha=3, eps=1e-7):
# Returns tsqrt_he IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
# change iou into pow(iou+eps)
# iou = inter / union
iou = torch.pow(inter/union + eps, alpha)
# beta = 2 * alpha
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = (cw ** 2 + ch ** 2) ** alpha + eps # convex diagonal
rho_x = torch.abs(b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2)
rho_y = torch.abs(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2)
rho2 = ((rho_x ** 2 + rho_y ** 2) / 4) ** alpha # center distance
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha_ciou = v / ((1 + eps) - inter / union + v)
# return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha_ciou) # CIoU
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)) # CIoU
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
# c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
# return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
c_area = torch.max(cw * ch + eps, union) # convex area
return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha) # GIoU
else:
return iou # torch.log(iou+eps) or iou
步骤2:配置loss.py文件
在utils / loss.py文件中找到__call__函数,将Regression loss中计算IoU的代码(如下图所示)。

换成下面这句:
iou = bbox_alpha_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, alpha=3, CIoU=True)🚀5.SIoU
💥💥5.1 简介
SIoU Loss 是指 Structural Similarity-based Intersection over Union Loss,它是一种用于计算目标检测任务中的损失函数。SIoU Loss 综合考虑了目标框的位置、尺度和形状信息,能够更准确地评估预测框与真实框之间的相似度。
在传统的目标检测任务中,常用的损失函数是交并比(Intersection over Union, IoU)损失。然而,IoU 损失只关注预测框和真实框的重叠度,未考虑到它们之间的结构相似性。因此,当目标框存在尺度、位置或形状变化时,IoU 损失可能会导致训练不稳定或者不准确。
为了解决这个问题,SIoU Loss 引入了结构相似性度量(Structural Similarity,SSIM)的概念。SSIM 是一种图像质量评价指标,用于衡量两个图像之间的结构相似性。在目标检测中,SIoU Loss 利用 SSIM 来度量预测框和真实框之间的结构相似性,并将其作为一个权重因子与传统的 IoU 损失相乘,从而得到最终的损失函数。

论文题目:《SIOU LOSS: MORE POWERFUL LEARNING FOR BOUNDING BOX REGRESSION》
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2205/2205.12740.pdf
💥💥5.2 添加步骤
步骤1:配置metrics.py文件
将utils / metrics.py文件中的bbox_iou函数全部替换成如下代码。
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, SIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns the IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU or SIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if SIoU: # SIoU Loss https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12740.pdf
s_cw = (b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) * 0.5
s_ch = (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) * 0.5
sigma = torch.pow(s_cw ** 2 + s_ch ** 2, 0.5)
sin_alpha_1 = torch.abs(s_cw) / sigma
sin_alpha_2 = torch.abs(s_ch) / sigma
threshold = pow(2, 0.5) / 2
sin_alpha = torch.where(sin_alpha_1 > threshold, sin_alpha_2, sin_alpha_1)
# angle_cost = 1 - 2 * torch.pow( torch.sin(torch.arcsin(sin_alpha) - np.pi/4), 2)
angle_cost = torch.cos(torch.arcsin(sin_alpha) * 2 - np.pi / 2)
rho_x = (s_cw / cw) ** 2
rho_y = (s_ch / ch) ** 2
gamma = angle_cost - 2
distance_cost = 2 - torch.exp(gamma * rho_x) - torch.exp(gamma * rho_y)
omiga_w = torch.abs(w1 - w2) / torch.max(w1, w2)
omiga_h = torch.abs(h1 - h2) / torch.max(h1, h2)
shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)
return iou - 0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost)
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 +
(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center distance squared
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
else:
return iou # IoU
步骤2:配置loss.py文件
在utils / loss.py文件中找到__call__函数,将Regression loss中计算IoU的代码(如下图所示)。

换成下面这句:
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, SIoU=True)
🚀6.WIoU
💥💥6.1 简介
WIoU Loss是一种用于计算目标检测任务中的损失函数。WIoU代表Weighted Intersection over Union,是Intersection over Union的变体。IoU是目标检测中常用的评估指标之一,用于衡量预测框与真实目标框之间的重叠程度。
WIoU Loss通过引入权重来平衡预测框的不同部分对损失的贡献。在计算IoU时,对预测框和真实目标框的每个像素进行二值化处理,然后计算重叠区域的像素个数。WIoU Loss通过将不同部分的权重乘以对应的像素个数,得到了加权的IoU。
使用WIoU Loss可以提高模型对目标边界的精确性,在训练过程中更加关注目标的边界预测。这对于一些需要准确目标边界的任务,如细粒度目标检测,尤为重要。
公式:
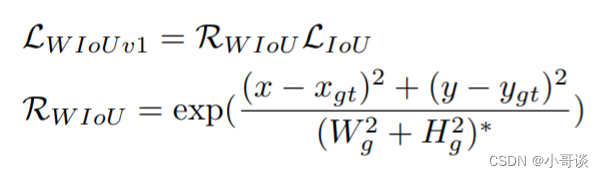

论文题目:《Wise-IoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism》
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.10051v1.pdf
💥💥6.2 添加步骤
步骤1:配置metrics.py文件
将utils / metrics.py文件中的bbox_iou函数全部替换成如下代码。
class WIoU_Scale:
''' monotonous: {
None: origin v1
True: monotonic FM v2
False: non-monotonic FM v3
}
momentum: The momentum of running mean'''
iou_mean = 1.
monotonous = False
_momentum = 1 - 0.5 ** (1 / 7000)
_is_train = True
def __init__(self, iou):
self.iou = iou
self._update(self)
@classmethod
def _update(cls, self):
if cls._is_train: cls.iou_mean = (1 - cls._momentum) * cls.iou_mean + \
cls._momentum * self.iou.detach().mean().item()
@classmethod
def _scaled_loss(cls, self, gamma=1.9, delta=3):
if isinstance(self.monotonous, bool):
if self.monotonous:
return (self.iou.detach() / self.iou_mean).sqrt()
else:
beta = self.iou.detach() / self.iou_mean
alpha = delta * torch.pow(gamma, beta - delta)
return beta / alpha
return 1
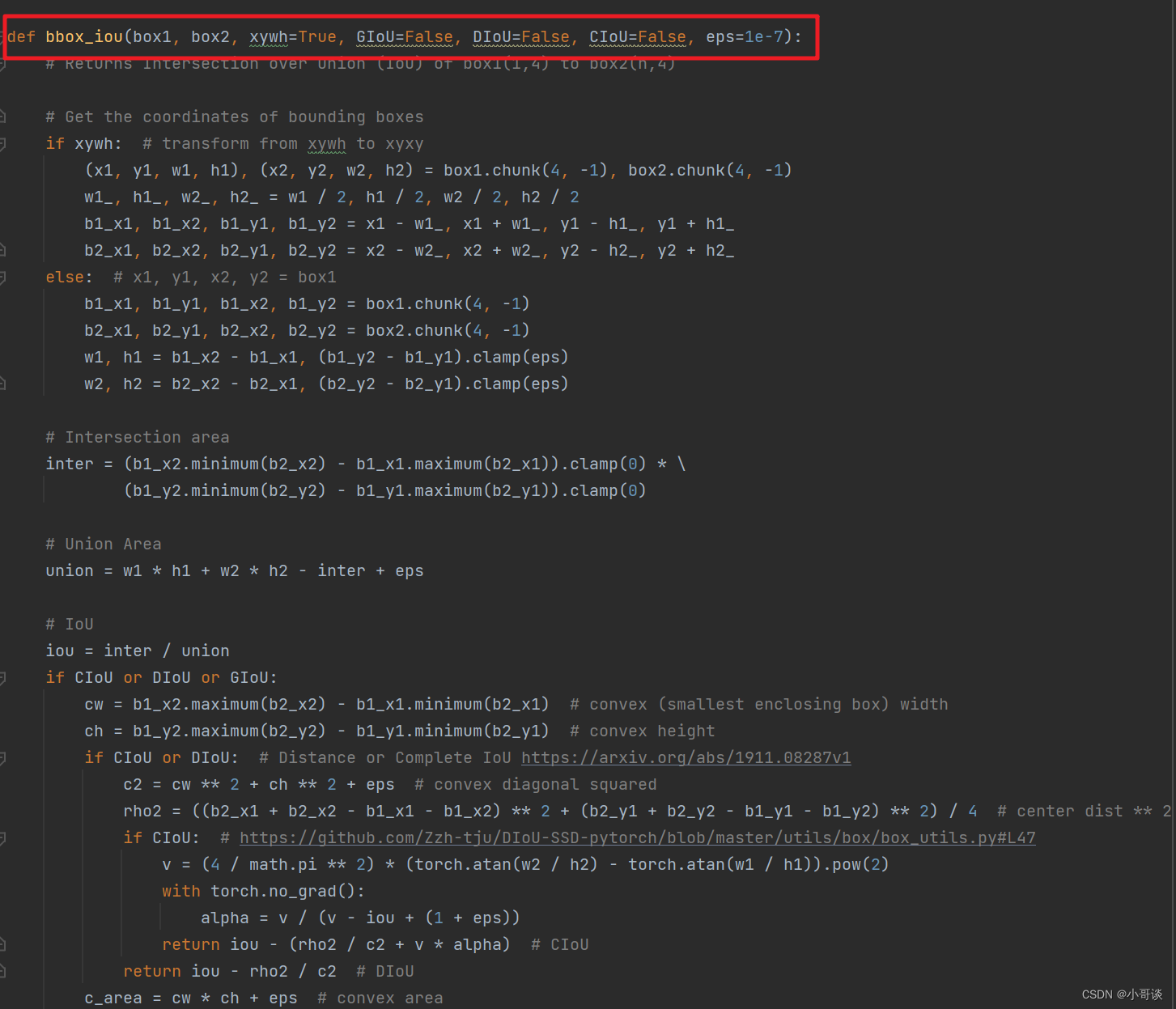
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, SIoU=False, EIoU=False, WIoU=False, Focal=False, alpha=1, gamma=0.5, scale=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns Intersection over Union (IoU) of box1(1,4) to box2(n,4)
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if xywh: # transform from xywh to xyxy
(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, -1), box2.chunk(4, -1)
w1_, h1_, w2_, h2_ = w1 / 2, h1 / 2, w2 / 2, h2 / 2
b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - w1_, x1 + w1_, y1 - h1_, y1 + h1_
b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - w2_, x2 + w2_, y2 - h2_, y2 + h2_
else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1.chunk(4, -1)
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2.chunk(4, -1)
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, (b1_y2 - b1_y1).clamp(eps)
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, (b2_y2 - b2_y1).clamp(eps)
# Intersection area
inter = (b1_x2.minimum(b2_x2) - b1_x1.maximum(b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(b1_y2.minimum(b2_y2) - b1_y1.maximum(b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
if scale:
self = WIoU_Scale(1 - (inter / union))
# IoU
# iou = inter / union # ori iou
iou = torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), alpha) # alpha iou
if CIoU or DIoU or GIoU or EIoU or SIoU or WIoU:
cw = b1_x2.maximum(b2_x2) - b1_x1.minimum(b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = b1_y2.maximum(b2_y2) - b1_y1.minimum(b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU or EIoU or SIoU or WIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = (cw ** 2 + ch ** 2) ** alpha + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = (((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4) ** alpha # center dist ** 2
if CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * (torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)).pow(2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha_ciou = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
if Focal:
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)), torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_CIoU
else:
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)) # CIoU
elif EIoU:
rho_w2 = ((b2_x2 - b2_x1) - (b1_x2 - b1_x1)) ** 2
rho_h2 = ((b2_y2 - b2_y1) - (b1_y2 - b1_y1)) ** 2
cw2 = torch.pow(cw ** 2 + eps, alpha)
ch2 = torch.pow(ch ** 2 + eps, alpha)
if Focal:
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + rho_w2 / cw2 + rho_h2 / ch2), torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_EIou
else:
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + rho_w2 / cw2 + rho_h2 / ch2) # EIou
elif SIoU:
# SIoU Loss https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12740.pdf
s_cw = (b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) * 0.5 + eps
s_ch = (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) * 0.5 + eps
sigma = torch.pow(s_cw ** 2 + s_ch ** 2, 0.5)
sin_alpha_1 = torch.abs(s_cw) / sigma
sin_alpha_2 = torch.abs(s_ch) / sigma
threshold = pow(2, 0.5) / 2
sin_alpha = torch.where(sin_alpha_1 > threshold, sin_alpha_2, sin_alpha_1)
angle_cost = torch.cos(torch.arcsin(sin_alpha) * 2 - math.pi / 2)
rho_x = (s_cw / cw) ** 2
rho_y = (s_ch / ch) ** 2
gamma = angle_cost - 2
distance_cost = 2 - torch.exp(gamma * rho_x) - torch.exp(gamma * rho_y)
omiga_w = torch.abs(w1 - w2) / torch.max(w1, w2)
omiga_h = torch.abs(h1 - h2) / torch.max(h1, h2)
shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)
if Focal:
return iou - torch.pow(0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost) + eps, alpha), torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_SIou
else:
return iou - torch.pow(0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost) + eps, alpha) # SIou
elif WIoU:
if Focal:
raise RuntimeError("WIoU do not support Focal.")
elif scale:
return getattr(WIoU_Scale, '_scaled_loss')(self), (1 - iou) * torch.exp((rho2 / c2)), iou # WIoU https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10051
else:
return iou, torch.exp((rho2 / c2)) # WIoU v1
if Focal:
return iou - rho2 / c2, torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_DIoU
else:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
if Focal:
return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha), torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
else:
return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha) # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
if Focal:
return iou, torch.pow(inter/(union + eps), gamma) # Focal_IoU
else:
return iou # IoU步骤2:配置loss.py文件
在utils / loss.py文件中找到__call__函数,将Regression loss中的代码(如下图所示)。
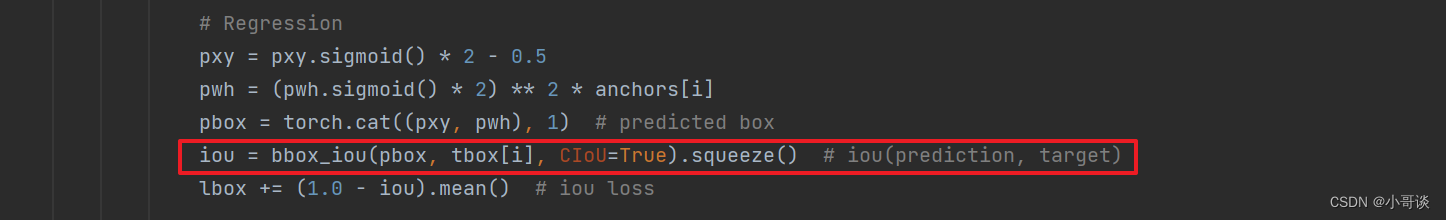
换成下面这句:
# WIoU
iou = bbox_iou(pbox, tbox[i], WIoU=True, Focal=False, scale=True)