浅拷贝:简单的赋值拷贝包含指针拷贝
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
//深拷贝、浅拷贝
//浅拷贝:简单的赋值拷贝包含指针拷贝
//深拷贝:在堆区重新申请的空间,进行拷贝操作
class Persion
{
public:
Persion()
{
cout << "无参构造函数!" << endl;
}
Persion(int age,int height)
{
this->m_Age = age;
cout << "有参构造函数!" << endl;
}
/*Persion(const Persion& p)
{
m_Height = p.m_Height;
cout << "拷贝构造函数!" << endl;
}*/
~Persion()
{
cout << "默认析构函数!" << endl;
}
int m_Age = 0;
int* m_Height;
};
Persion test01()
{
Persion p1(10,20);
Persion p2(p1);//调用拷贝构造函数,如果没有,编译器会提供一个默认的拷贝构造函数,这里发生的是浅拷贝
cout << "p1的值:" << p1.m_Age << endl;
cout << "p2的值:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
return p2;
}
void main()
{
test01();
}深拷贝:在堆区重新申请的空间,进行拷贝操作
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
//深拷贝、浅拷贝
//浅拷贝:简单的赋值拷贝包含指针拷贝
//深拷贝:在堆区重新申请的空间,进行拷贝操作
class Persion
{
public:
Persion()
{
cout << "无参构造函数!" << endl;
}
Persion(int age, int height)
{
this->m_Age = age;
//在堆区开辟空间
m_Height = new int(height);
cout << "有参构造函数!" << endl;
}
Persion(const Persion& p)
{
m_Age = p.m_Age;
//当调用拷贝构造函数的时候,把拷贝对象的值在堆区重新开辟空间
m_Height = new int(*p.m_Height);
}
~Persion()
{
//释放堆区内存
if (m_Height != NULL)
{
delete this->m_Height;
this->m_Height = NULL;
}
cout << "默认析构函数!" << endl;
}
int m_Age = 0;
int* m_Height;
};
Persion test01()
{
Persion p1(10, 20);
Persion p2(p1);//调用拷贝构造函数,如果没有,编译器会提供一个默认的拷贝构造函数
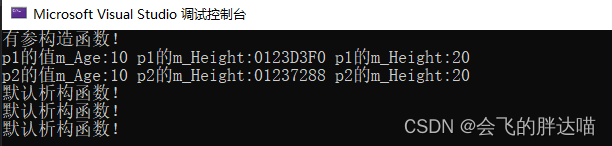
cout << "p1的值m_Age:" << p1.m_Age << " p1的m_Height:" << p1.m_Height << " p1的m_Height:" << *p1.m_Height << endl;
cout << "p2的值m_Age:" << p2.m_Age << " p2的m_Height:" << p2.m_Height << " p2的m_Height:" << *p2.m_Height << endl;
return p2;
}
void main()
{
Persion p = test01();
}这里调用了三次析构函数
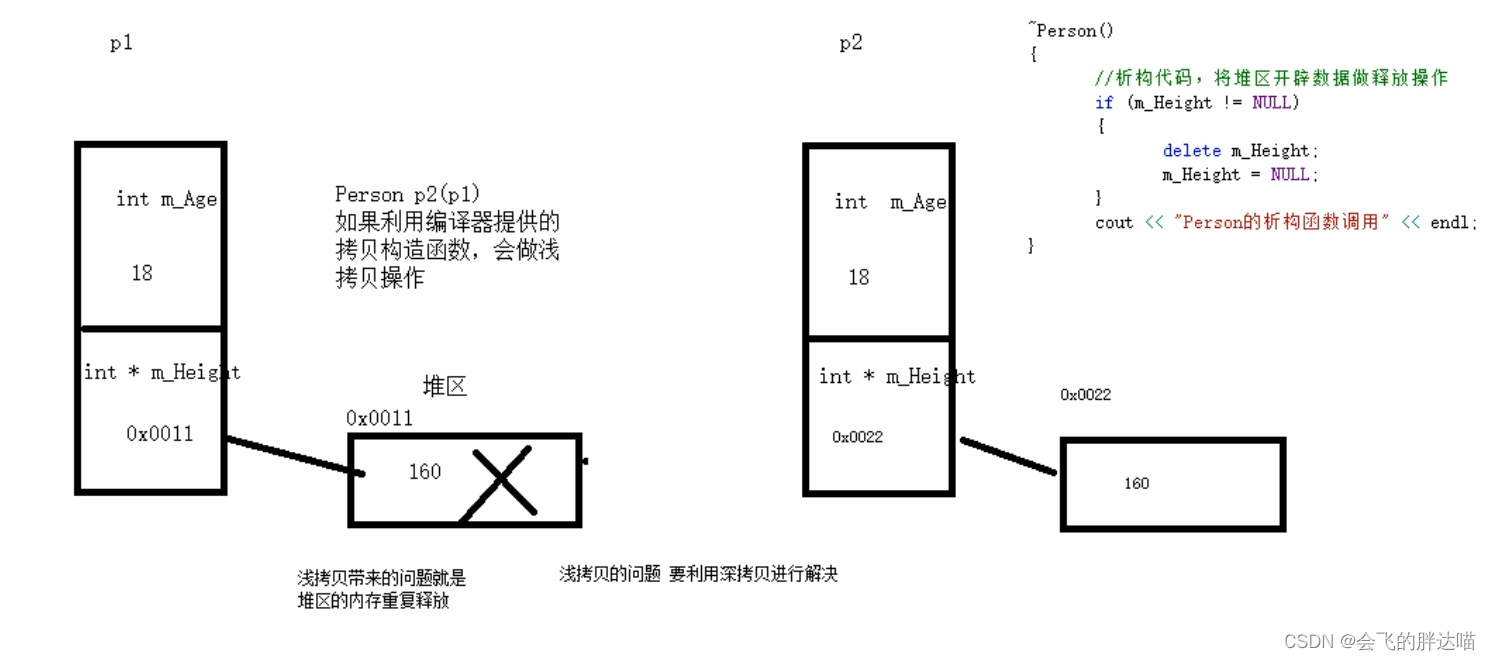
原理图





![[每周一更]-(第61期):Rust入门策略(持续更新)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b58ef74f2335447296942335b335182d.jpeg#pic_center)